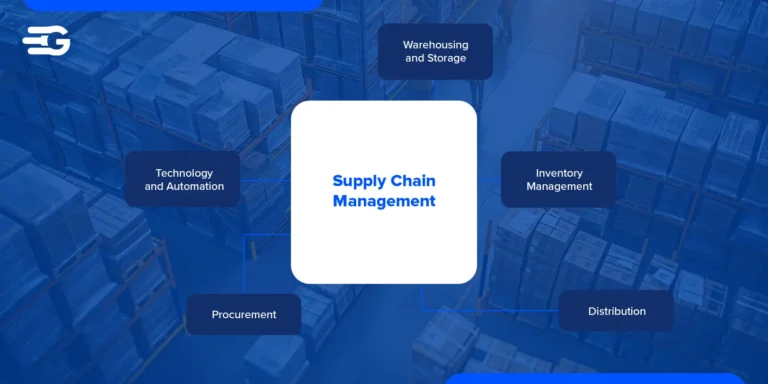
4 Types of Logistics Management
Logistics management is the backbone of any efficient supply chain. It involves planning, controlling, and executing the movement of goods, services, and information from the point of origin to the point of consumption. Effective logistics management is vital for business continuity and ensuring that supply chain operations run seamlessly. Understanding the different types of logistics is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize operations and enhance customer satisfaction.
The four primary types of logistics management are inbound logistics, outbound logistics, reverse logistics, and third-party logistics (3PL). Each type plays a distinct role in the logistics processes, and mastering them can significantly impact overall supply chain efficiency. By strategically managing these types, companies can minimize disruptions, improve efficiency, and ultimately provide better customer service.
Inbound Logistics
Inbound logistics refers to the process of receiving, storing, and managing incoming goods or materials from suppliers. It is a fundamental part of supply chain logistics, as it ensures that essential resources are available when needed, contributing to smooth production and operational efficiency. Without efficient inbound logistics, manufacturing processes can face delays, resulting in productivity loss and increased costs.
Key Activities
- Sourcing raw materials from reliable suppliers.
- Transportation from suppliers to manufacturing facilities.
- Receiving and warehousing products to maintain stock levels.
- Inventory management to ensure availability without overstocking.
Importance
Efficient inbound logistics are vital for maintaining a consistent production flow. Delays or mismanagement can disrupt manufacturing, affecting the entire supply chain logistics. Businesses that implement strategic inbound logistics, like Interlake Mecalux, can mitigate risks and maintain continuity in production. Implementing technology solutions, such as real-time tracking, can also help improve inbound logistics efficiency.
Outbound Logistics
Outbound logistics focuses on distributing finished products to customers. This process includes storage, transportation, and delivery, ensuring that products reach their destination in a timely and efficient manner. Effective outbound logistics enhance customer satisfaction by providing reliable and fast delivery, which is increasingly important in today’s competitive market.
Key Activities
- Order processing to accurately fulfill customer requests.
- Packaging and labeling to ensure product safety and brand consistency.
- Transportation to customers via reliable logistics partners.
- Delivery tracking to keep customers informed.
Importance
Outbound logistics directly impacts customer satisfaction. Companies that streamline their outbound processes, like Tassgroup, experience improved logistics operations and enhanced service quality. In a world where delivery speed influences purchasing decisions, investing in robust outbound logistics systems can be a competitive advantage.
Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics handles the return, repair, recycling, or disposal of goods. It manages the flow of products back from customers or end-users to the manufacturer or disposal point. As businesses focus more on sustainability, reverse logistics has become an integral part of modern logistics management.
Key Activities
- Product returns handling to manage customer complaints or faulty items.
- Recycling and disposal of materials to support environmental initiatives.
- Refurbishment and resale to reduce waste and recover costs.
- Warranty recovery to manage defective goods effectively.
Importance
Reverse logistics contributes to cost reduction and supports sustainability efforts. Effective management helps recapture value and reduce waste. Companies like Investopedia highlight how strategic reverse logistics can boost a company’s reputation and reduce environmental impact. Emphasizing reverse logistics also helps businesses align with circular economy practices.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Third-party logistics involves outsourcing logistics functions to specialized providers. This approach allows businesses to focus on core operations while leveraging external expertise. Choosing the right 3PL partner can significantly enhance logistics efficiency, especially for businesses looking to expand their distribution network.
Key Services
- Transportation and freight forwarding to facilitate global trade.
- Warehousing and distribution for efficient inventory management.
- Inventory management to track stock levels and minimize shortages.
- Order fulfillment to manage customer demands promptly.
Importance
By partnering with a 3PL provider, companies can improve logistics efficiency without the burden of managing logistics in-house. Ennilogistics and other leaders in the field offer tailored solutions to meet specific business needs. Additionally, 3PLs provide flexibility to scale logistics operations as business requirements evolve.
Conclusion
Understanding the four types of logistics management is essential for optimizing supply chain performance. By efficiently managing inbound, outbound, reverse, and third-party logistics, businesses can ensure seamless operations and deliver better customer experiences. Integrating these logistics types can significantly reduce operational costs, improve efficiency, and boost service quality.
For more insights on logistics management and strategies to enhance efficiency, check out our Comprehensive Guide to Logistics Management. Leveraging best practices in logistics can position businesses to thrive amid evolving market demands.